Introduction
Description
In coding or software engineering, we manipulate data. Most of the time, we are dealing with some sort of input data, whether it be a list of strings, numbers, graphs of user connections, etc. On that data we need to perform specific actions and return the result output that might be displayed to the user of stored somewhere.
Manipulating data involves structuring that data, organizing, and managing it. The correct choice of data structure allows major improvements in program efficiency.
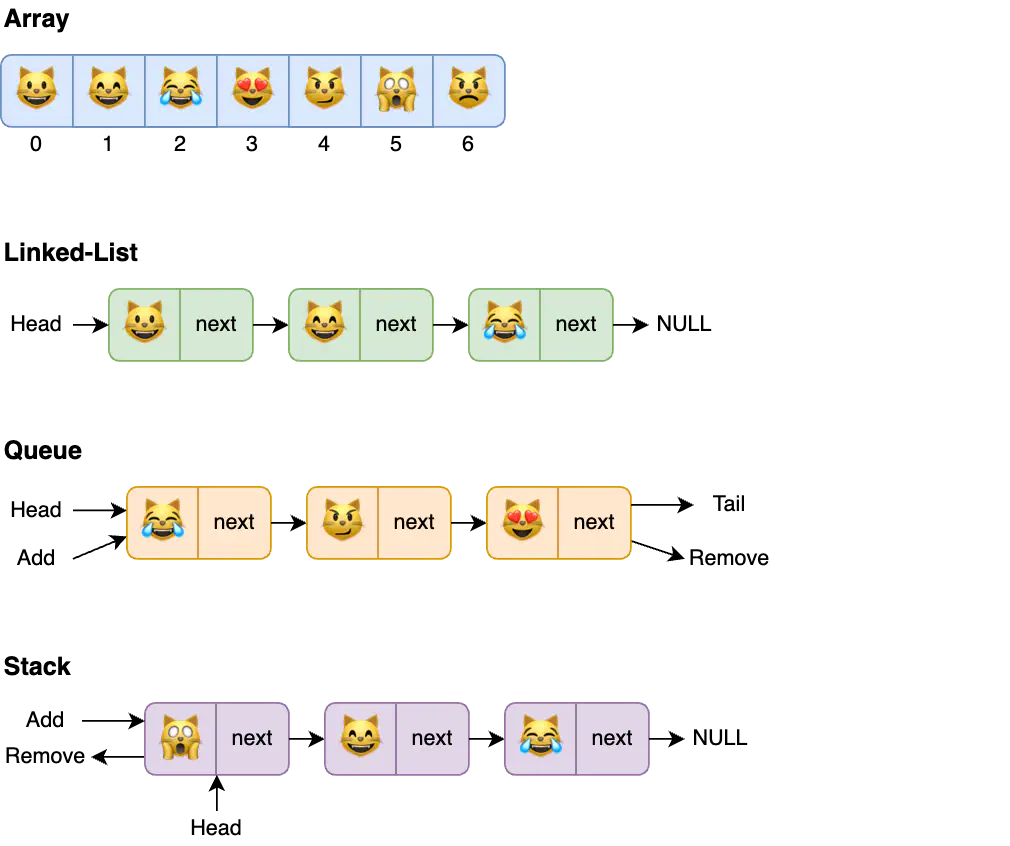
A Data Structure is an arrangement of data in computer’s memory. Data structures include arrays, queues, linked lists, stacks, graphs, and others.
Classification
The data structure can be linear or non-linear, depending on how elements are stored.
Linear Data Structures
In this kind of data structure, the elements are stored sequentially (one after the other). These structures are typically easy to implement but they can be inefficient for data access operations. The common examples of liner structures are array, linked-list, stack, and queue.
Linear data structures might be static or dynamic in terms of memory usage:
- A Static data structure has a fixed memory size, making accessing its elements easier. The example is an array.
- Dynamic data structures do not fix memory size but determine the required amount in runtime. It allows us to use memory space efficiently and extend it on demand. Examples: queue, stack, and linked-list.
Non-Linear Data Structures
Elements of non-linear data structures are not stored in an ordered sequence. Instead, they are stored in a specific hierarchy where one element can be connected to a few others. In this case, we cannot traverse all the elements in a single run. Examples: tree and graph.

Overview
| Data Structure | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Array | Quick insertion Quick access by index | Slow search Slow deletion Fixed size |
| Ordered Array | Quicker search than unsorted array | Slow insertion and deletion Fixed size |
| Stack | Provides last-in, first-out access | Slow access to other items |
| Queue | Provides first-in, last-out access | Slow access to other items |
| Linked List | Quick insertion, deletion | Slow search |
| Binary Tree | Quick search, insertion | Complex deletion |
| Red-Black Tree | Quick search, insertion, deletion Tree always balanced | Complex |
| 2-3-4 Tree | Quick search, insertion, deletion Tree always balanced | Complex |
| Hash Table | Fast access for known key Fast insertion | Slow, if key isn’t known Inefficient memory usage |
| Heap | Fast insertion, deletion Fast access to largest item | Slow access to other items |
| Graph | Models real-world situations | Some algorithms are slow and complex |