Stack
Overview
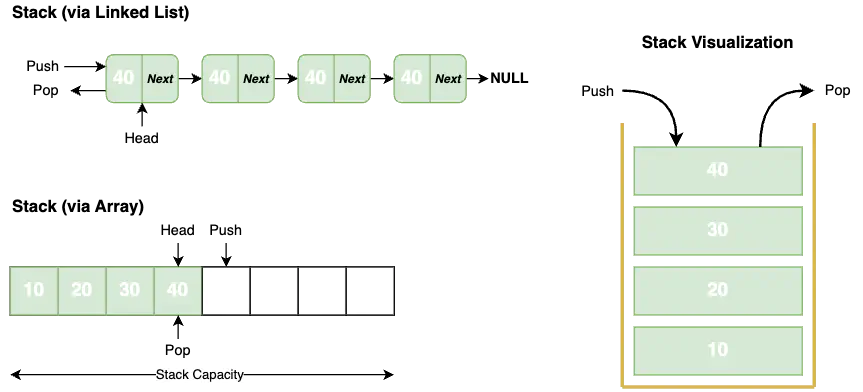
A Stack is a linear data structure where the elements are inserted and removed in a particular order. Stack examines the item most recently added - LIFO (Last In, First Out).
- A Stack can be implemented with either an array or a linked list.
- Each stack operation takes constant time (
O(1)).
Stack Types
- Fixed Size. It has a predefined capacity and cannot be re-sized dynamically in runtime. If the stack is full, pushing a new element will cause an overflow error.
- Dynamic size. It can adjust its capacity based on the number of stored elements. It can be implemented using a re-sizable array or a linked list.
Operations
| Operation | Description | Time Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Push | Insert an element at the top of the stack | O(1) |
| Peek | Retrieve the top element of the stack without removing it | O(1) |
| Pop | Retrieve the top element of the stack and removing it | O(1) |
| Size | Get the number of elements in the stack | O(1) |
Advantages
- Easy to implement
- It has a lot of applications in different algorithms
Disadvantages
- Random accessing is not possible
- Requires extra memory for pointers if implemented as a LinkedList
- It doesn’t provide a dynamic size if implemented as an Array
Use Cases
- Program execution stack trace (nested and recursive function calls)
- Backtracking (find the path through a maze)
- Depth-First Search
- Implementing Undo/Redo operations in various editor apps
- Balanced Brackets (check if all the opened brackets are closed)
- Browser history navigation
Implementation
To implement the Stack, we need to maintain a pointer referring to the top element.
public class StackArray<T> {
private T[] stack;
private int headIndex = -1;
// Initialize stack with a custom capacity
public StackArray(int capacity) {
stack = (T[]) new Object[capacity];
}
// Insert a new element onto the stack
public void push(T value) {
stack[++headIndex] = value;
}
// Retrieve the top element and delete it
public T pop() {
T value = stack[headIndex];
stack[headIndex--] = null;
return value;
}
// Retrieve the top element without deleting it
public T peek() {
return stack[headIndex];
}
}
public class StackLinkedList<T> {
private class Node {
public T value;
public Node next;
}
private Node head;
// Insert a new element onto the stack
public void push(T value) {
Node node = new Node();
node.value = value;
node.next = head;
head = node;
}
// Retrieve the top element and delete it
public T pop() {
T value = head.value;
head = head.next;
return value;
}
// Retrieve the top element without deleting it
public T peek() {
return head.value;
}
}
The complete StackArray and StackLinkedList implementations are available here.
Built-in Examples
Stack<String> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push("First");
stack.push("Second");
stack.push("Third");
stack.peek(); // "Third"
stack.pop(); // "Third"
stack.size(); // 2
stack.empty(); // false
stack.firstElement(); // "First"
stack.lastElement(); // "Second"
stack.capacity(); // 10
Deque<String> stack = new ArrayDeque<>();
stack.push("First");
stack.push("Second");
stack.push("Third");
stack.peek(); // "Third"
stack.pop(); // "Third"
stack.size(); // 2
stack.isEmpty(); // false
stack.peekLast(); // "First"
stack.peekFirst(); // "Second"
stack.getLast(); // "First"
stack.getFirst(); // "Second"
const stack: string[] = [];
stack.push("First");
stack.push("Second");
stack.push("Third");
stack[stack.length - 1]; // "Third"
stack.pop(); // "Third"
stack.length; // 2
stack.length === 0; // false